Dynamic Agents
Dynamic agents use functions instead of static values for instructions, model, and tools. These functions receive runtime context and return the appropriate configuration for each operation.
When you call generateText() or streamText(), the agent resolves dynamic values using the context map you provide. This lets you configure agent behavior per-request based on user roles, subscription tiers, language preferences, or any custom logic.
Use Cases
Dynamic agents work well for:
- Multi-tenant applications where different users need different capabilities
- Role-based access control where admins get different tools than regular users
- Subscription tiers where premium users get access to different models
- Internationalization where responses adapt to user's language
- A/B testing where different users get different configurations
How Dynamic Resolution Works
When you provide a function instead of a static value, the agent calls it during each operation:
- You call
agent.generateText(input, { context }) - Agent invokes your function with
DynamicValueOptions - Function receives
{ context, prompts }and returns the value - Agent uses the resolved value for that operation
The resolution happens in agent.ts:2583-2606 via the resolveValue() method. Dynamic functions are called on every operation, so keep them synchronous or fast.
Type System
Dynamic values use the DynamicValue<T> type:
type DynamicValue<T> = (options: DynamicValueOptions) => Promise<T> | T;
interface DynamicValueOptions {
context: Map<string | symbol, unknown>; // Runtime context you provide
prompts: PromptHelper; // VoltOps prompt management
}
The agent defines three specific dynamic types:
InstructionsDynamicValue:string | DynamicValue<string | PromptContent>ModelDynamicValue<T>:T | DynamicValue<T>ToolsDynamicValue:(Tool | Toolkit)[] | DynamicValue<(Tool | Toolkit)[]>
Basic Example
Here's a dynamic agent that changes instructions based on user role:
import { Agent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const dynamicAgent = new Agent({
name: "Adaptive Assistant",
// Dynamic instructions based on user context
instructions: ({ context }) => {
const role = (context.get("role") as string) || "user";
const language = (context.get("language") as string) || "English";
if (role === "admin") {
return `You are an admin assistant with special privileges. Respond in ${language}.`;
} else {
return `You are a helpful assistant. Respond in ${language}.`;
}
},
model: openai("gpt-4o"),
});
Dynamic Properties
You can make instructions, model, and tools dynamic. Each is resolved independently during operation execution.
Dynamic Instructions
Instructions can be a string or a function that returns a string (or PromptContent when using VoltOps).
const agent = new Agent({
name: "Multilingual Support Agent",
instructions: ({ context }) => {
const language = (context.get("language") as string) || "English";
const supportTier = (context.get("supportTier") as string) || "basic";
let baseInstructions = `You are a customer support agent. Respond in ${language}.`;
if (supportTier === "premium") {
baseInstructions += " You can offer advanced troubleshooting and priority support.";
} else {
baseInstructions += " Provide standard support within basic guidelines.";
}
return baseInstructions;
},
model: openai("gpt-4o"),
});
Dynamic Models
The model can be a static LanguageModel or a function returning one. The agent resolves the model at agent.ts:1672 before each generation call.
const agent = new Agent({
name: "Tier-Based Assistant",
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.",
// Different models for different subscription tiers
model: ({ context }) => {
const tier = (context.get("tier") as string) || "free";
switch (tier) {
case "premium":
return openai("gpt-4o");
case "pro":
return openai("gpt-4o-mini");
default:
return openai("gpt-3.5-turbo");
}
},
});
Dynamic Tools
Tools can be a static array or a function returning an array. The agent stores dynamic tool functions separately in the dynamicTools property (agent.ts:337) and resolves them at agent.ts:1673.
import { createTool } from "@voltagent/core";
import { z } from "zod";
// Regular user tool
const basicTool = createTool({
name: "get_help",
description: "Get basic help information",
parameters: z.object({
topic: z.string().describe("Help topic"),
}),
execute: async ({ topic }) => {
return `Here's basic help about ${topic}`;
},
});
// Admin-only tool
const adminTool = createTool({
name: "admin_action",
description: "Perform administrative actions",
parameters: z.object({
action: z.string().describe("Admin action to perform"),
}),
execute: async ({ action }) => {
return `Admin action performed: ${action}`;
},
});
const agent = new Agent({
name: "Role-Based Agent",
instructions: "You are an assistant with role-based capabilities.",
// Different tools based on user role
tools: ({ context }) => {
const role = (context.get("role") as string) || "user";
if (role === "admin") {
return [basicTool, adminTool]; // Admins get both tools
} else {
return [basicTool]; // Regular users get basic tools only
}
},
model: openai("gpt-4o"),
});
Execution
Pass context as an option to any generation method. The agent uses this context to resolve dynamic values:
// Create context with relevant information
const context = new Map<string, unknown>();
context.set("role", "admin");
context.set("language", "Spanish");
context.set("tier", "premium");
context.set("company", "TechCorp");
// Generate response with context
const response = await dynamicAgent.generateText("Help me manage the system settings", {
context,
});
console.log(response.text);
// The agent will respond in Spanish, with admin capabilities,
// using the premium model, and have access to admin tools
You can also use it with streaming:
const streamResponse = await dynamicAgent.streamText("What products are available?", {
context: new Map([
["role", "customer"],
["language", "French"],
["tier", "basic"],
]),
});
for await (const chunk of streamResponse.textStream) {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
}
REST API Usage
You can pass context via the REST API to trigger dynamic resolution over HTTP.
API Request Format
Pass the context object within the options field of your API request:
{
"input": "Your message to the agent",
"options": {
"context": {
"role": "admin",
"language": "Spanish",
"tier": "premium"
},
"temperature": 0.7,
"maxTokens": 500
}
}
REST API Examples
Basic Text Generation:
# Admin user requesting help in Spanish
curl -X POST http://localhost:3141/agents/YOUR_AGENT_NAME/text \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": "I need to update system settings",
"options": {
"context": {
"role": "admin",
"language": "Spanish",
"tier": "enterprise"
}
}
}'
Streaming with Real-time Context:
# Stream response for different user roles
curl -N -X POST http://localhost:3141/agents/YOUR_AGENT_NAME/stream \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": "Write a summary of our quarterly results",
"options": {
"context": {
"role": "manager",
"department": "finance",
"accessLevel": "confidential",
"language": "English"
}
}
}'
VoltOps Integration
The VoltOps dashboard lets you test dynamic agents by setting context values through a visual interface.
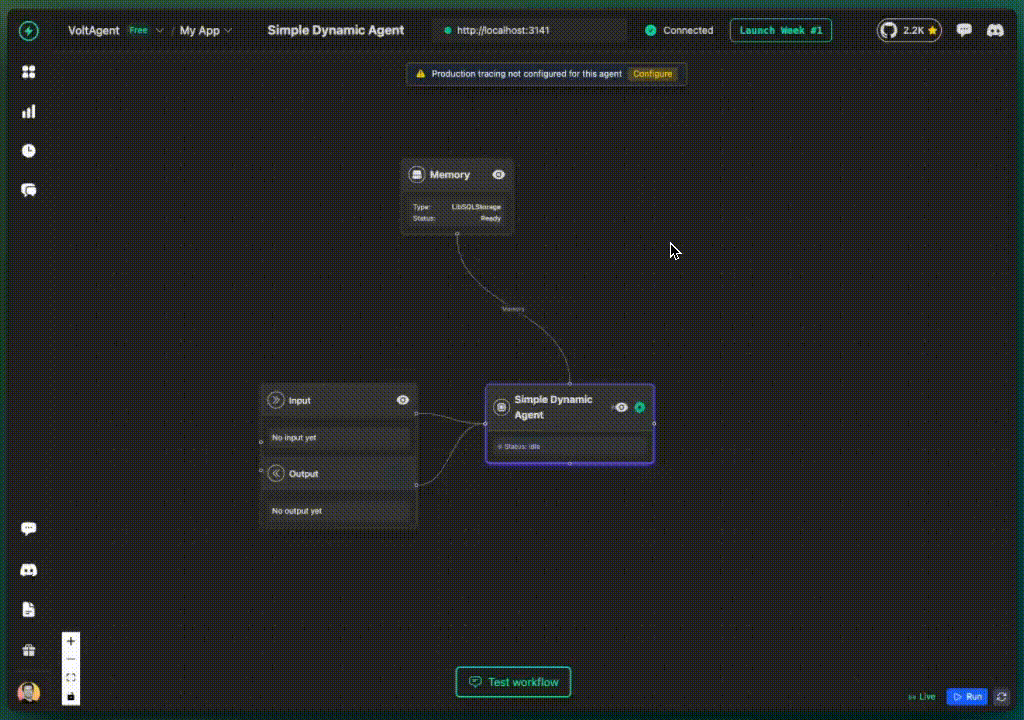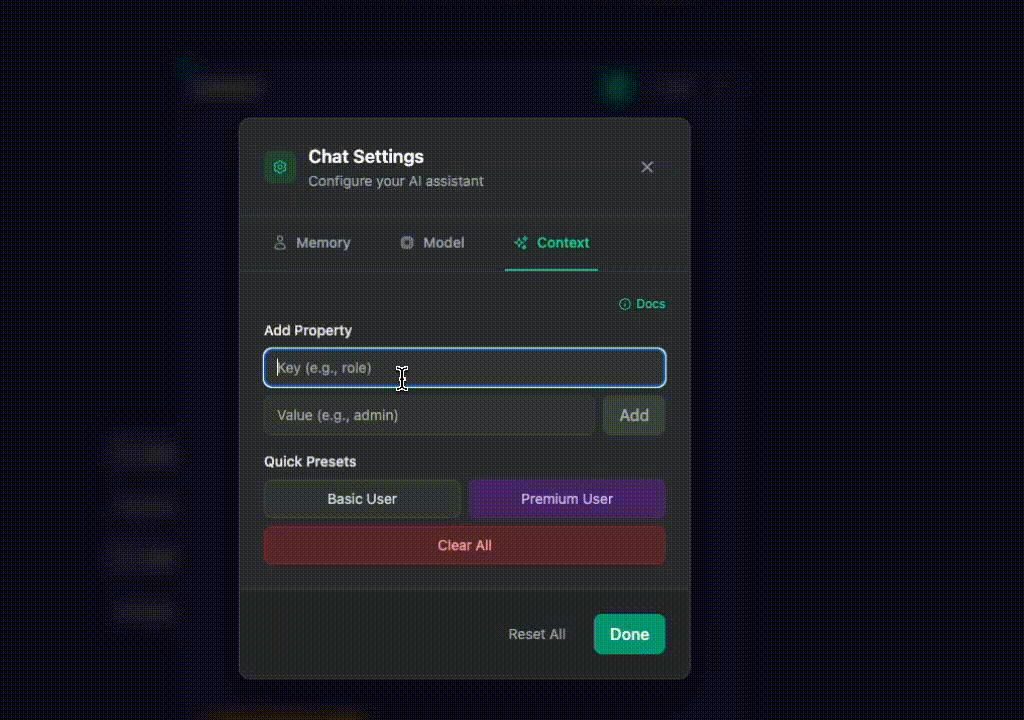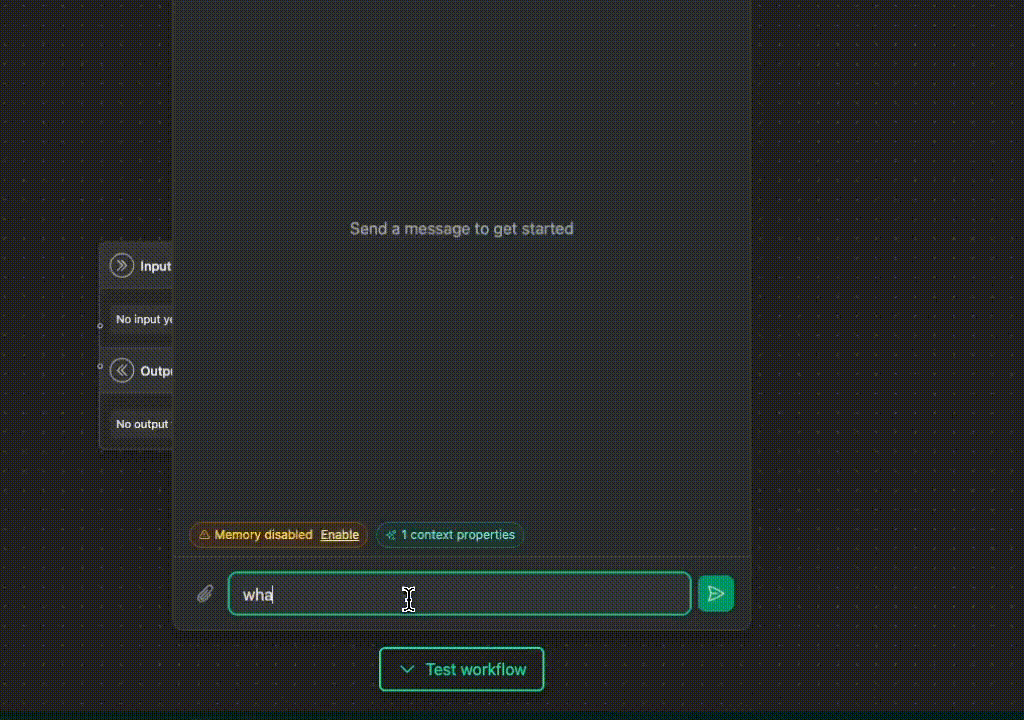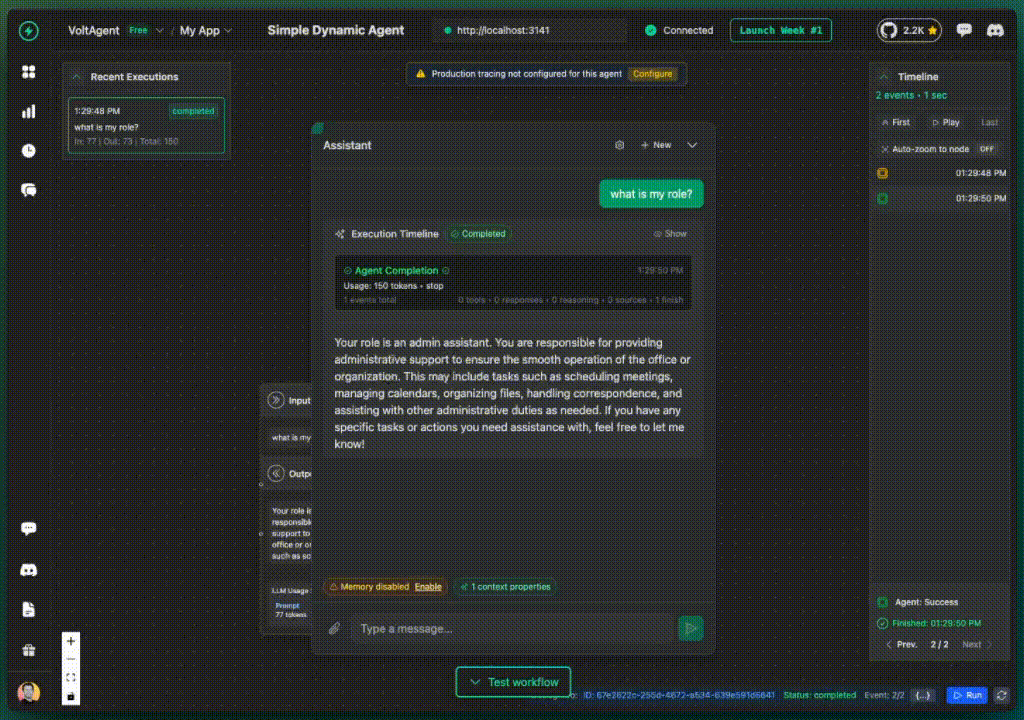
You can:
- Set context values through a form
- Test different user roles and configurations
- Monitor how dynamic properties change based on context
- Debug dynamic agent logic
Best Practices
Context Validation
Validate context values and provide defaults:
instructions: ({ context }) => {
// Always provide defaults and validate types
const role = (context.get("role") as string) || "user";
const language = (context.get("language") as string) || "English";
// Validate known values
const validRoles = ["admin", "support", "customer"];
const actualRole = validRoles.includes(role) ? role : "customer";
return `You are a ${actualRole} assistant. Respond in ${language}.`;
};
Performance
Dynamic functions run on every operation. Avoid async operations or heavy computation:
// ✅ Good - Fast synchronous logic
model: ({ context }) => {
const tier = context.get('tier') as string;
return tier === 'premium' ? openai('gpt-4o') : openai('gpt-3.5-turbo');
},
// ❌ Avoid - API calls or database queries
model: async ({ context }) => {
const userProfile = await fetchUserFromDatabase(context.get('userId'));
return determineModelFromProfile(userProfile);
}
Security
Use allowlists for security-sensitive values:
instructions: ({ context }) => {
const role = context.get("role") as string;
// ✅ Use allowlists for security-sensitive operations
const allowedRoles = ["admin", "support", "customer"];
const safeRole = allowedRoles.includes(role) ? role : "customer";
return `You are a ${safeRole} assistant.`;
};
Context Structure
Use consistent context key naming across your application:
// ✅ Consistent naming convention
const createUserContext = (user: User) => {
const context = new Map<string, unknown>();
context.set("user.id", user.id);
context.set("user.role", user.role);
context.set("user.tier", user.subscriptionTier);
context.set("user.language", user.preferredLanguage);
context.set("request.timestamp", Date.now());
return context;
};
Advanced Patterns�
Conditional Resolution
Make properties dynamic only when context requires it:
const agent = new Agent({
name: "Conditionally Dynamic Agent",
// Static instructions most of the time
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.",
// But dynamic model when user context is provided
model: ({ context }) => {
// If no tier specified, use default static model
if (!context.has("tier")) {
return openai("gpt-4o-mini"); // Default model
}
// Otherwise, choose based on tier
const tier = context.get("tier") as string;
return tier === "premium" ? openai("gpt-4o") : openai("gpt-3.5-turbo");
},
// model is selected dynamically above
});
Context Between Operations
Pass the same context to related operations for consistency:
// Main agent with context
const parentResponse = await dynamicAgent.generateText("Create a summary", {
context: myContext,
});
// Sub-agent inherits the same context
const detailResponse = await detailAgent.generateText(
"Provide more details",
{ context: myContext } // Same context for consistency
);
Error Handling
Wrap dynamic logic in try-catch and provide fallbacks:
model: ({ context }) => {
try {
const tier = context.get("tier") as string;
if (tier === "premium") {
return openai("gpt-4o");
}
return openai("gpt-3.5-turbo");
} catch (error) {
console.warn("Error in dynamic model selection:", error);
// Fallback to safe default
return openai("gpt-3.5-turbo");
}
};